Many digital code lock circuits have been published in this magazine. In those circuits a set of switches (conforming to code) are pressed one by one within the specified time to open the lock. In some other circuits, custom-built ICs are used and positive and negative logic pulses are keyed in sequence as per the code by two switches to open the lock.
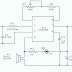
Digital Code Lock Circuit diagram :

A low-cost digital code lock circuit is presented in this article. Here the keying-in code is rather unique. Six switches are to be pressed to open the lock, but only two switches at a time. Thus a total of three sets of switches have to be pressed in a particular sequence. (Of these three sets, one set is repeated.) The salient features of this circuit are:
1. Use of 16 switches, which suggests that there is a microprocessor in-side.
2. Elimination of power amplifier transistor to energise the relay.
3. Low cost and small PCB size.
An essential property of this electronic code lock is that it works in monostable mode, i.e. once triggered, the output becomes high and remains so for a period of time, governed by the timing components, before returing to the quiescent low state. In this circuit, timer IC 555 with 8 pins is used. The IC is inexpensive and easily available. Its pin 2 is the triggering input pin which, when held below 1/3 of the sup-ply voltage, drives the output to high state. The threshold pin 6, when held higher than 2/3 of the supply voltage, drives the output to low state. By applying a low-going pulse to the reset pin 4, the output at pin 3 can be brought to the quiescent low level. Thus the reset pin 4 should be held high for normal operation of the IC.
Three sets of switches SA-SC, S1-S8 and S3-S4 are pressed, in that order, to open the lock. On pressing the switches SA and SC simultaneously, capacitor C3 charges through the potential divider comprising resistors R3 and R4, and on releasing these two switches, capacitor C3 starts discharging through resistor R4. Capacitor C3 and resistor R4 are so selected that it takes about five seconds to fully discharge C3.
Depressing switches S1 and S8 in unison, within five seconds of releasing the switches SA and SC, pulls pin 2 to ground and IC 555 is triggered. The capacitor C1 starts charging through resistor R1. As a result, the output (pin 3) goes high for five seconds (i.e. the charging time T of the capacitor C1 to the threshold voltage, which is calculated by the relation T=1.1 R1 x C1 seconds). Within these five seconds, switches SA and SC are to be pressed momentarily once again, followed by the depression of last code-switch pair S3-S4.
These switches connect the relay to out-put pin 3 and the relay is energised. The contacts of the relay close and the solenoid pulls in the latch (forming part of a lock) and the lock opens. The remaining switches are connected between reset pin 4 and ground. If any one of these switches is pressed, the IC is re-set and the output goes to its quiescent low state. Possibilities of pressing these reset switches are more when a code breaker tries to open the lock.
LED D5 indicates the presence of power supply while resistor R5 is a cur-rent limiting resistor.
The given circuit can be recoded easily by rearranging connections to the switches as desired by the user.
Source : www.ecircuitslab.com