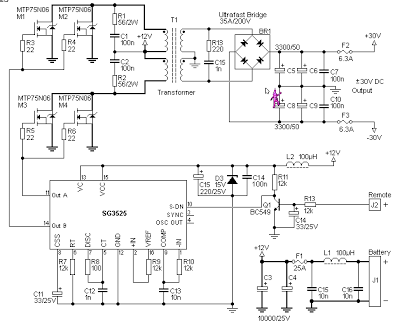
This simple to build alarm can be fitted in bikes to protect them from being stolen. The tiny circuit can be hidden anywhere, without any complicated wiring. Virtually, it suits all bikes as long as they have a battery. It doesnt drain out the battery though as the standby current is zero. The hidden switch S1 can be a small push-to-on switch, or a reed switch with magnet, or any other similar simple arrangement. The circuit is designed around a couple of low-voltage MOSFETs configured as monostable timers. Motorbike key S2 is an ignition switch, while switch S3 is a tilt switch. Motorbike key S2 provides power supply to the gate of MOSFET T2, when turned on.
When you turn ignition off using key S2, you have approximately 15 seconds to get off the bike; this function is performed by resistor R6 to discharge capacitor C3. Thereafter, if anyone attempts to get on the bike or move it, the alarm sounds for approximately15 seconds and also disconnects the ignition circuit. During parking, hidden switch S1 is normally open and does not allow triggering of mosfet T1. But when someone starts the motorbike through ignition switch S2, MOSFET T2 triggers through diode D1 and resistor R5. Relay RL1 (12V, 2C/O) energises to activate the alarm (built around IC1) as well as to disconnect the ignition coil from the circuit. Disconnection of the ignition coil prevents generation of spark from the spark plug. Usually, there is a wire running from the alternator to the ignition coil, which has to be routed through one of the N/C1 contacts of relay RL1 as shown in Fig.1 Fig.2 shows the pin configurations of SCR BT169, MOSFET BS170 and transistor BC548.
Circuit diagram :
Motorbike Alarm Circuit Diagram
Motorbike Alarm-Pin Configurations :
Pin configurations of BT169, BS170 and BC548
Also, on disconnection of the coil, sound generator IC UM3561 (IC1) gets power supply through N/O2 contact of relay RL1. This drives the darlington pair built around T3 and T4 to produce the siren sound through loudspeaker LS1. To start the vehicle, both hidden switch S1 and ignition key S2 should be switched on. Otherwise, the alarm will start sounding. Switching on S1 triggers SCR1, which, in turn, triggers MOSFET T1. MOSFET T1 is configured to disable MOSFET T2 from functioning. As a result, MOSFET T2 does not trigger and relay RL1 remains de-energised, alarm deactivated and ignition coil connected to the circuit. Connection to the ignition coil helps in generation of spark from the spark plug. Keeping hidden switch S1 accessible only to the owner prevents the bike from pillaging. Tilt switch S3 prevents attempt to move the vehicle without starting it. Glass-and metal-bodied versions of the switch offer bounce-free switching and quick break action even when tilted slowly.
Unless otherwise stated, the angle by which the switch must be tilted to ensure the contact operation (operating angle), must be approximately 1.5 to 2 times the stated differential angle. The differential angle is the measure of the just closed position to the just open position. The tilt switch has characteristics like contacts make and break with vibration, return to the open state at rest, non-position sensitivity, inert gas and hermetic sealing for protection of contacts and tin-plated steel housing. If you find difficulty in getting the tilt switch, you may replace it with a reed switch (N/O) and a piece of magnet. The magnet and the reed switch should be mounted such that the contacts of the switch close when the bike stand is lifted up from rest.
Streamcircuits

 Pin configurations of moc3021, bt136 and 5v regulator 7805
Pin configurations of moc3021, bt136 and 5v regulator 7805 








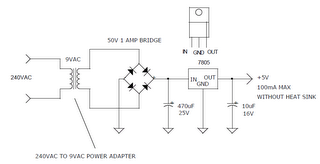
 A lower charging current just brings about a correspondingly longer charge time. IMHO 100mA is quite low, low enough that the circuit can be used for an overnight charger for many typical single-cell li-ion batteries. The resistors are deliberately kept at large orders of magnitude (tens/hundred Kohm and Mohm range) to keep the off-state current as low as possible, at about 2?A. Resistor tolerances should be kept at 1% for output voltage accuracy. The 50k pot allows for an output voltage range between 4.08V to 4.26V - thus allowing calibration as well as a choice between a charging voltage of 4.1V or 4.2V depending on the cell to be charged. The capacitors are for stability, especially C2 which prevents the output from ringing/oscillating.
A lower charging current just brings about a correspondingly longer charge time. IMHO 100mA is quite low, low enough that the circuit can be used for an overnight charger for many typical single-cell li-ion batteries. The resistors are deliberately kept at large orders of magnitude (tens/hundred Kohm and Mohm range) to keep the off-state current as low as possible, at about 2?A. Resistor tolerances should be kept at 1% for output voltage accuracy. The 50k pot allows for an output voltage range between 4.08V to 4.26V - thus allowing calibration as well as a choice between a charging voltage of 4.1V or 4.2V depending on the cell to be charged. The capacitors are for stability, especially C2 which prevents the output from ringing/oscillating. A Low Cost hearing Aid Circuit
A Low Cost hearing Aid Circuit