Strip LEDs are available in different colours powered by direct current (DC) source. These LEDs are available as surface mount devices with current limiting resistors. Usually there are 300 LEDs in a 5-metre strip. The strip can be cut into pieces so that the bits having three or four LEDs can be used with 12V DC source. The circuit given here uses the strip LEDs to make an automatic white LED lighting source.
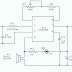
Simple Strip LED Lamp Circuit diagram:

The circuit is powered by a capacitor power supply connected to AC mains. Capacitor C1 drops the 230V AC, which is further rectified by the bridge rectifier module and is made ripple-free by C2. Zener diode (ZD1) provides 12V DC to the comparator circuit. Resistor R1 is important in the power supply as it provides discharge path to the voltage stored in capacitor C1 after the circuit is unplugged from mains.
The automatic working of the circuit is based on the light-sensing property of the light-dependent resistor (LDR). Operational amplifier CA3140 (IC1) is used as a comparator with two potential dividers in its inverting and non-inverting inputs. LDR1 and resistor R3 form one potential divider that provides a variable voltage at the inverting input pin 2 of IC1. Second potential divider comprises resistors R4 and R5, which provide half of the supply voltage (6V) to the non-inverting pin 3 of IC1. The output of IC1 depends on voltage level at inverting input pin 2 of IC1 as explained below.
In daylight, LDR1 has low resistance and the voltage at inverting input (pin 2) of IC1 is more than that of non-inverting input (pin 3). This makes IC1 output low, which drives transistor T1 into cut-off condition and strip LEDs do not glow. However, at night the light incident on LDR1 is low and its resistance is high. The voltage at inverting input of the comparator decreases, making it lower than the voltage at non-inverting input. This makes IC1 output high. Transistor T1 goes into saturation, thus connecting cathodes of LEDs to ground. All the LEDs in the strip turn on and remain that way till morning.
Assemble the circuit on a general-purpose PCB and enclose it in a suit-able shock-proof case. Strip LEDs are available in ribbon-shaped form. Use 5cm bits (two bits) having three LEDs each. The strip can be cut at supply-contact points. Strip LEDs are arranged on a flexible belt with double-sided adhesive on the back side, so it can be glued to any surface. Connect the LED strip in the circuit with correct polarity.
EFY note. Since the circuit uses 230V AC, there is a risk of electrical shock. Do not touch or troubleshoot when the circuit is plugged in.Before connecting the circuit to the power supply section, test it using 12V DC from a battery or DC power supply.
Source: http://www.ecircuitslab.com/2012/05/simple-strip-led-lamp.html